Guide To Lose Fat: A Detailed Overview
Published On : 27th Nov 2024

Achieving sustainable fat loss involves adopting a diet and lifestyle that promotes a calorie deficit while maintaining nutrient balance. This guide provides evidence-based strategies, food choices, and tips to help you lose fat effectively.
What we are covering here:
Understand the Basics of Fat Loss
To lose fat, you need to consume fewer calories than your body burns, creating a calorie deficit. Fat loss is a process that involves creating a consistent calorie deficit while preserving muscle mass and maintaining overall health.

- Energy Balance: The foundation of fat loss is energy balance:
- Calories In: The calories you consume from food and drinks.
- Calories Out: The calories your body uses for energy, including Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) in which calories burned at rest to maintain vital functions , Physical Activity in which calories burned through movement and exercise, Thermic Effect of Food (TEF) in which energy used to digest and metabolize food.
To lose fat, you must consume fewer calories than your body burns, creating a calorie deficit.
- Macronutrients: Understanding macronutrients helps optimize fat loss while preserving muscle and energy:
- Protein: It supports muscle retention during calorie restriction and helps reduce hunger by increasing satiety. Protein sources are like Lean meats, eggs, dairy, legumes, tofu.
- Carbohydrates: It is the primary source of energy, especially for active individuals. Choose complex carbs (whole grains, vegetables) for sustained energy and fiber.
- Fats: Essential for hormone production and brain health. Focus on healthy fats (avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil).
- The Science of Fat Storage and Burning: When you consume more calories than you burn, the excess is stored as fat. In a calorie deficit, your body taps into stored fat for energy, leading to fat loss. Sustainable fat loss targets 0.5-1% of your body weight per week.
Importance Of Metabolism in Fat Loss
Metabolism plays a central role in determining how effectively your body burns calories, regulates energy, and ultimately supports fat loss. It refers to the biochemical processes in your body that convert food into energy. This energy fuels essential functions such as breathing, circulation, and physical activity.
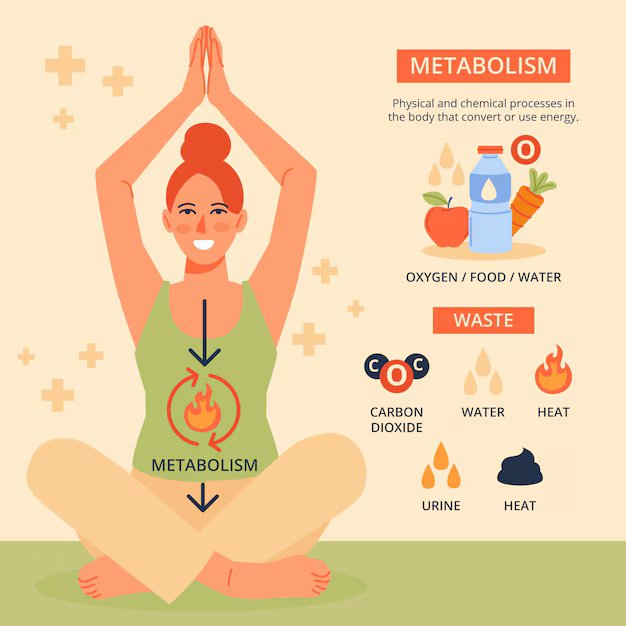
- How Metabolism Influences Fat Loss: A faster metabolism burns more calories, making fat loss easier. Conversely, a slower metabolism requires more effort to create a calorie deficit. Extended reduction in caloric intake can result in decreased metabolism as the body adjusts to save energy, commonly known as "metabolic adaptation."
-
Factors Affecting Metabolism: Factors that determine our metabolic rate includes:
- Age: Metabolic rate declines with age due to loss of muscle mass and hormonal changes.
- Body Composition: More muscle mass leads to a higher BMR, while higher fat mass lowers it.
- Genetics: Some people naturally have faster or slower metabolisms.
- Hormones: Hormones like thyroid hormones, insulin, and cortisol regulate metabolic processes.
- Activity Level: Regular exercise and daily movement increase calorie burn and boost metabolism.
-
Optimizing Metabolism for Fat Loss: To maximize metabolism and support fat loss:
- Engage in strength training 2-4 times a week.
- Consume adequate protein to maintain muscle during calorie restriction.
- Incorporate both structured exercise (e.g., cardio, resistance training) and NEAT (e.g., walking, taking stairs).
- Protein has the highest thermic effect of food, aiding metabolism and satiety.
- Aim for a moderate calorie deficit of 10-20% below maintenance.
- Drinking water can temporarily boost metabolism by up to 30% for about an hour.
Metabolism is a vital factor in fat loss, but it is not the sole determinant. Combining a calorie deficit with muscle-building exercises, protein-rich meals, and consistent physical activity will optimize your metabolic rate and support sustainable fat loss.
Best Foods for Fat Loss
When aiming for fat loss, choosing nutrient-dense, satiating, and metabolism-boosting foods can make the journey more effective and enjoyable.

-
Lean Proteins: High-protein foods are essential for muscle preservation, metabolism, and satiety and includes Eggs, Fish, Tofu, Low-Fat Dairy like Greek Yogurt, cottage cheese and milk.
-
Healthy Fats: Fats help regulate hormones and keep you full longer. It includes Avocado, Olive oil which is good for healthy heart, Nuts & Seeds like Almonds, walnuts & chia seeds.
-
Fiber-Rich Vegetables: Low in calories and high in volume, vegetables are perfect for staying full. It includes Spinach, broccoli, cauliflower, brussels sprouts, zucchini, cucumbers, carrots & bell peppers.
-
Fruits: Fruits provide natural sweetness, fiber, and essential nutrients which includes Berries, Apples which are high in fiber & water content, Oranges & Grapefruit which are rich in Vitamin C and Bananas which are great for pre-workout energy and muscle recovery.

-
Whole Grains: Complex carbohydrates provide energy and fiber for digestion. Have Quinoa which is a complex protein and rich in fiber, Oats which are perfect for breakfast, Brown Rice, Whole grain Bread & Pasta.
-
Legumes and Beans: High in protein, fiber, and complex carbs. It includes Lentils which is great for soups & salads, Chickpeas, Black Beans & Kidney Beans.
-
Hydration and Calorie-Free Beverages: Staying hydrated is essential for fat loss. It includes Water, Green Tea which improves metabolism and boost fat oxidation, Black Coffee and Herbal Teas.
These all are best foods for fat loss and there is one more thing, Apple Cider Vinegar which by consuming in the early morning empty stomach helps in fat loss rapidly.
Foods to Avoid or Limit
While no food is inherently "bad," some are less conducive to achieving fat loss due to their high calorie density, low nutrient value, or potential to promote overeating. Moderation is key, but avoiding or limiting the following foods can enhance your fat loss efforts.

-
Sugary snacks and desserts: These are high in calories but low in nutrients, they cause blood sugar spikes and crashes, leading to increased hunger. Examples : Chocolates, Candies, Sweets, Cakes, Pastries, Ice Cream and other sugary desserts.

-
Processed and fried foods: These are high in unhealthy fats and calories, these foods can lead to overeating and contribute to inflammation. Examples : French fries, onion rings, fried chicken, Potato chips, Fast food burgers and other fried items.
-
Refined Carbohydrates: Stripped of fiber and nutrients, refined carbs are digested quickly, leading to rapid blood sugar spikes and reduced satiety. Examples : White bread, white pasta, white rice, Crackers and other refined-grain snacks.
-
High-Calorie Condiments and Sauces: They can add hidden calories and unhealthy fats to meals. Examples : Mayonnaise, creamy salad dressings, cheese sauces, Ketchup, barbecue sauce, Syrups and heavy gravies.
By avoiding or limiting these foods, you can maintain a calorie deficit, control hunger, and achieve your fat loss goals more effectively.
Common Diet Patterns for Fat Loss
Various diet patterns can help with fat loss by promoting a calorie deficit and emphasizing nutrient-dense foods.

-
Intermittent Fasting (IF): Time-restricted eating patterns alternating between fasting and eating windows.
-
Popular Methods- 16:8: 16-hour fast, 8-hour eating window, 5:2: Eat normally for 5 days, restrict calories to 500-600 for 2 days.
-
Benefits- Simplifies calorie control, may improve insulin sensitivity.
-
Challenges- Hunger during fasting periods, not suitable for everyone.
-
Low-Carbohydrate Diet (e.g., Keto, Atkins): Minimize carbs, increase fats, moderate protein. Low carbs promote fat burning as the body enters ketosis (keto) or relies on fat stores for energy.
-
Food Examples- Meat, fish, eggs, low-carb vegetables, nuts, seeds.
-
Benefits- Rapid initial weight loss, reduced appetite.
-
Challenges- May lead to nutrient deficiencies if poorly planned, not suitable for everyone.
-
Mediterranean Diet: Emphasizes whole foods, healthy fats, lean proteins, and moderate carbs.
-
Food Examples- Olive oil, fish, nuts, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes.
-
Benefits- Sustainable, heart-healthy, rich in nutrients.
-
Challenges- Weight loss may be slower due to moderate calorie intake.
-
Plant-Based Diets (e.g., Vegetarian, Vegan): Centered on plant-derived foods; some include dairy or eggs. Whole, fiber-rich plant foods improve satiety and nutrient intake.
-
Food Examples- Vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, seeds, tofu.
-
Benefits- May lower calorie density, improve overall health.
-
Challenges- Requires planning to meet protein and nutrient needs.
Belly Fat and Strategies to reduce Belly Fat
While overall body fat is a health concern, visceral fat, located around essential organs in the abdomen, is a more serious issue. Researchers have linked these fats to a higher risk of developing a range of health issues, such as heart diseases, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic disorders.

Your eating habits play a crucial role in the accumulation of excess belly fat. Consuming a lot of refined carbohydrates, added sugars, and unhealthy fats is likely to result in increased storage of belly fat. Additionally, consuming too many calories, having compromised gut health, and leading a sedentary lifestyle can accelerate the buildup of belly fat.
-
Strategies to reduce Belly Fat: Some fibers plays a crucial role in fighting against bloating in the stomach which helps with increasing a sense of satiety, regulating blood sugar levels, and improving digestion. The top sources include oats, barley, legumes, apples, oranges, Brussels sprouts, and carrots in the vegetable category. Reducing the amount of added sugars and refined carbs you consume should be top priority in order to reduce belly fat. Below are a few useful recommendations:
-
Thoroughly examine the nutrition labels of items on your shopping list and select the ones with the lowest amount of added sugars.
-
Eat whole grains instead of consuming refined grains like white bread and pasta. By doing this, you will receive sufficient fiber.
- Substitute candies and drinks such as soda and juice with water, unsweetened teas, and fruit beverages.
- Engage in Regular Exercise like Cardio(Running,cycling,swimming), Strength Training(Weight lifting, bodyweight exercises).
Sample Diet Plan
A sample diet plan to create a calorie deficit, which provide balanced nutrition, and support sustained energy levels throughout the day. Adjust portions based on your individual caloric needs and activity level.

-
Breakfast Ideas:
-
Egg and Veggie Scramble with Greek Yogurt.
-
Avocado Toasts with Eggs
-
Veggie Omelet with a Banana
- Cooked Quinoa with Almond Milk
- Protein Smoothies made with Unsweetened almond milk, a scoop of protein powder, spinach, half a banana, and a tablespoon of almond butter.
-
Lunch Ideas:
-
Quinoa and Chickpea Salad having Quinoa, chickpeas, spinach, diced peppers, and a lemon-tahini dressing.
-
Grilled Chicken Salad having Mixed greens, grilled chicken breast, cherry tomatoes, cucumbers, avocado slices, and a light olive oil vinaigrette.
-
Tofu and Veggie Stir-Fry made with Sautéed tofu, broccoli, bell peppers, zucchini, and mushrooms, served over cauliflower rice.
- Grilled Veggie Wrap made with Whole-grain tortilla with grilled zucchini, eggplant, hummus, and spinach.
- Chicken and Vegetable Soup having shredded chicken, carrots, celery, and spinach.
- Lentil Soup made with Lentils, diced tomatoes, onions, garlic, and a dash of cumin.
- Cauliflower Rice Bowl made with Cauliflower rice, sautéed vegetables, and a dash of soy sauce.
-
Dinner Ideas:
-
Grilled Chicken with Steamed Vegetables made with Chicken breast, steamed broccoli, carrots, and zucchini with a drizzle of olive oil or lemon.
-
Tofu Veggie Stir-Fry having Cubed tofu, snap peas, carrots, and mushrooms sautéed in sesame oil and garlic.
-
Lentil Stew made with Lentils, diced tomatoes, onions, garlic, and spinach.
- Chickpea and Spinach Curry made with Chickpeas, spinach, coconut milk (light), and curry spices, served over cauliflower rice.
- Tofu Stir-Fry with Vegetables made with Cubed tofu, broccoli, bell peppers, and sesame seeds, stir-fried in olive oil and garlic.
- 1 Chapati/Roti with any Lentil(Daal) along with vegetable salad having vinegar on top
-
Mid Day/Evening Snacks Ideas:
-
Greek yogurt with berries and almonds.
-
Apple Slices with Almond Butter
-
Nuts and Seeds like almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds.
- Fruits including Papaya, water melon, oranges.
- Banana and Peanut Butter.
- Herbal Tea with Almonds or Organic Green Tea
The Role of Exercise
While diet is key, exercise increases calorie burn, preserves lean muscle mass and improves overall health and well-being.

-
Cardio: Burns a significant number of calories and supports overall fat loss. HIIT, in particular, has been shown to burn fat effectively and improve metabolic health. Running, cycling, dancing, swimming (for 150-300 minutes weekly).
-
Strength Training: Builds muscle, increases metabolic rate, and preserves lean mass during weight loss. Weightlifting, bodyweight exercises(3-4 times a week)
-
Flexibility and Mobility Training: Improves recovery, reduces injury risk, and supports functional movement, which helps you perform other exercises more effectively. Yoga, Pilates, dynamic stretching. (Refer to beginner's yoga Here)












